Reports of ICE raids and deportations don’t just affect the individuals directly targeted. They ripple outward, with real consequences for community health and well-being.
Also in New York health news: Two cases of Legionnaires' disease in Harlem, code temps forecast, and the ripple effects of ICE in communities.
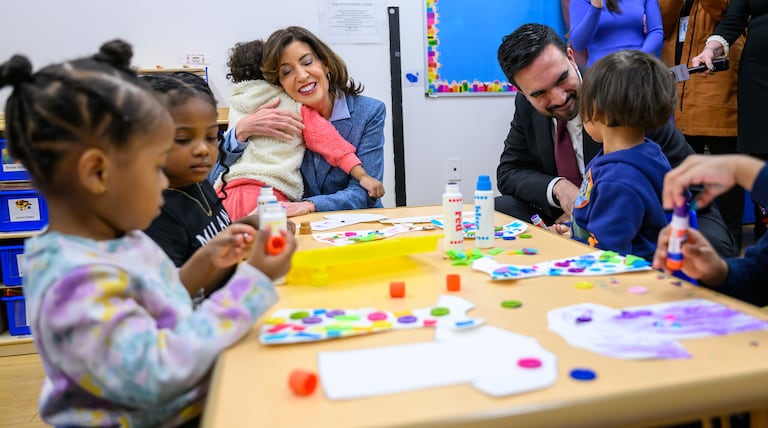
High-quality early care and education programs are associated with positive developmental outcomes for children, improved maternal mental health, and increased maternal employment.
The past year has been chaotic for public health, but here's a roundup of some noteworthy accomplishments.
As we head into the holidays and many of us travel to be with loved ones, there’s some health news to keep in mind.
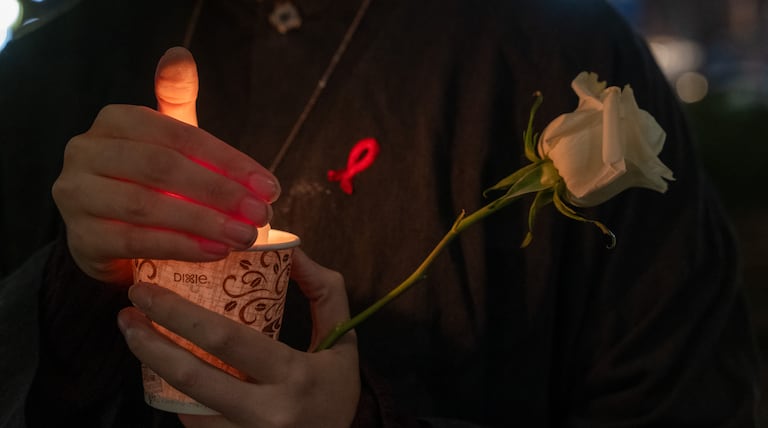
New York City has made incredible progress against HIV, but rising infection rates, persistent disparities, and looming federal funding cuts risk a backslide.
Meanwhile, flu and RSV cases are increasing across the city and state.
As we head into Thanksgiving, when many of us will be traveling to see loved ones, flu and RSV are top of mind. To reduce the spread of illness, consider masking in indoor crowded spaces.
The subsidies, introduced during the pandemic and later extended, made health insurance more affordable for millions. If they expire at the end of the year, health care will become more expensive for millions.
A new state health report finds fewer high school students are using cigarettes, e‑cigarettes, or other tobacco products last year.